AI-Powered FinTech: The Future of Financial Software Development
Table of Contents
Fintech, the fusion of finance and technology, is revolutionizing how we manage and interact with money. This dynamic sector has transformed traditional banking and investment methods, making financial services more accessible and efficient for everyone. But the real game-changer has been the introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into this mix.
AI is not just enhancing fintech; it’s redefining it by introducing advancements in financial software development. From automating complex processes to delivering personalized financial advice, AI’s impact is far-reaching. As we have entered into the era of digital transformation, the integration of AI in fintech is setting new standards for innovation and convenience in financial services. Want to know more about how AI is leading this charge and what it means for the future of financial software development? Read our blog.
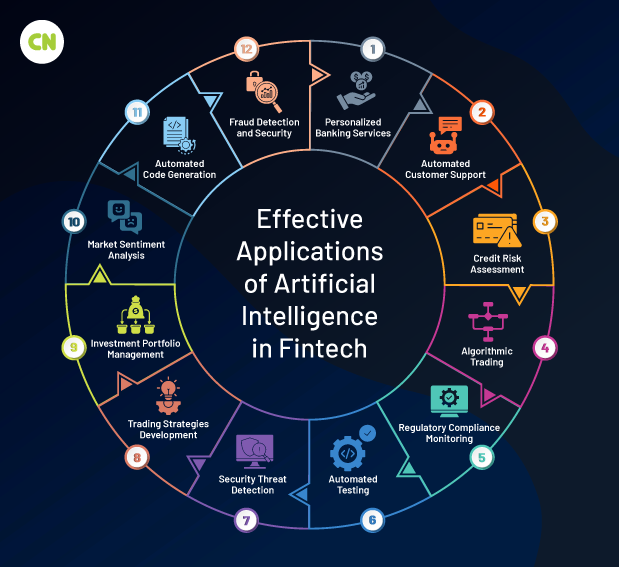
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Financial Software Development
- Automated Code GenerationAI-driven tools automatically generate code based on predefined parameters and requirements. It speeds up the development process and minimizes human errors. This ensures that the financial software developed is efficient and reliable. Automated code generation is useful for repetitive tasks and boilerplate code, freeing developers to focus on more complex problems.
- Fraud Detection and SecurityUsing machine learning algorithms, AI systems can sift through massive volumes of transactions in real-time. It helps identify patterns that may indicate fraudulent activity. By learning from historical fraud data, these systems get better at quickly recognizing even the smallest hints of fraud. It enhances the security of financial transactions and safeguards user data against unauthorized access.
- Personalized Banking ServicesAI analyzes individual user data, such as spending habits, income, and financial goals, to provide personalized banking advice and services. This could range from suggesting budgeting tips to recommending investment strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and engagement. Personalized services help banks and financial institutions build stronger customer relationships, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
- Automated Customer SupportThrough AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, financial institutions can offer 24/7 customer support, handling inquiries and resolving issues faster than humanly possible. These AI systems can understand and process natural language. They provide accurate responses and perform tasks such as account management or transaction inquiries, improving overall customer service efficiency.
- Credit Risk AssessmentAI models process vast amounts of data to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers with greater accuracy than traditional methods. AI can predict potential default risks by analyzing past transactions, spending behavior, and social media activity, allowing financial institutions to make more informed lending decisions. This reduces the risk of bad debt and enables competitive rates for low-risk customers.
- Algorithmic TradingBy analyzing market conditions, historical data, and current news, AI algorithms can execute trades at optimal times to maximize profits. Algorithmic trading can process complex market data at a speed impossible for human traders, identifying buying or selling opportunities based on predefined criteria and executing trades within milliseconds.
- Regulatory Compliance MonitoringAI tools continuously scan for changes in regulatory compliance requirements and automatically update systems to follow new regulations. This proactive approach reduces the risk of non-compliance, which can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage. AI-driven compliance monitoring ensures financial institutions remain up-to-date with the latest regulatory standards without manual oversight.
- Automated TestingAI enhances software testing by automatically running tests, identifying bugs, and suggesting fixes. It reduces the time and resources required for quality assurance, ensuring that financial software is reliable and secure before its release. Automated testing with AI can also adapt and learn from previous testing cycles, improving test coverage and efficiency over time.
- Security Threat DetectionAdvanced AI systems monitor networks in real-time, instantly detecting and responding to security threats. They can identify unusual behavior that could signify a cyber attack, such as data breaches or malware infections, and take preventive actions to mitigate risks. This real-time monitoring and response capability is critical in protecting financial data and customer information in an increasingly digital world.
- Trading Strategies DevelopmentAI analyzes vast amounts of market data to develop and refine trading strategies, helping traders and institutions to make informed decisions. These strategies can adapt to new data, learning from market trends and outcomes to optimize future trades. This dynamic approach to strategy development can lead to higher returns and lower risk.
- Investment Portfolio ManagementAI-driven portfolio management services analyze market data, risk preferences, and investment goals to optimize investment portfolios. They can automatically rebalance portfolios in response to market changes, ensuring that investment goals are met while adhering to risk tolerance levels.
- Market Sentiment AnalysisBy examining news articles, social media posts, and financial reports, AI can gauge the market’s sentiment toward particular stocks, sectors, or the overall market. This sentiment analysis can inform investment decisions, providing insights into potential market movements based on public perception and trends.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Biases
Ethical considerations in AI software development cannot be overlooked. Therefore, when integrating AI into financial software development, it’s essential to address ethical concerns alongside potential biases. While powerful, AI systems reflect the data they are trained on, which can mistakenly continue existing biases or create new ones. Here are some key points to consider:
Ethical Considerations
- Privacy and Data Protection: AI in finance often requires processing vast amounts of personal and sensitive data. Ensuring the privacy and protection of this data is vital, requiring strict compliance with data protection laws and ethical standards.
- Transparency: Financial institutions must strive for transparency in how AI algorithms make decisions, especially when those decisions affect customers’ financial health or access to services. It includes clear communication about the use of AI and the factors influencing its decisions.
- Accountability: There must be accountability for the decisions made by AI systems. When AI-driven decisions lead to negative outcomes, it’s important to have mechanisms for recourse and correction. It ensures that individuals can challenge decisions and seek redress.
Potential Biases
- Data Bias: AI models can inherit biases present in their training data. For example, if historical loan approval data reflects past discriminatory practices, the AI system might learn to replicate those biases, affecting fairness in loan approvals.
- Algorithmic Bias: The design and implementation of AI algorithms can also introduce bias. Developers must be vigilant in reviewing algorithms for potential biases and employ techniques to mitigate these risks.
- Feedback Loops: AI systems can create feedback loops where biased decisions reinforce the data, leading to increasingly biased outcomes. Identifying and interrupting these loops is crucial for preventing systemic biases.
How is AI Augmenting Developers?
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the software development process represents a shift towards augmenting the capabilities of human developers. AI’s role isn’t to replace humans but to enhance their efficiency, creativity, and decision-making processes. Here’s how AI is making a positive impact:
- Better Efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks, accelerates code generation, and streamlines workflows, allowing developers to focus on higher-value activities and reducing development time and costs.
- Enhanced Creativity: By handling routine tasks, AI frees developers to channel their creativity into solving complex problems and exploring innovative approaches in financial software development. This creates a culture of innovation within development teams, creating more robust and inventive solutions.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: AI-driven insights help developers allocate resources more efficiently in financial software development projects by identifying areas with the highest potential for optimization or improvement.
- Improved Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data precisely and accurately. It minimizes errors in financial software development and ensures the reliability and integrity of the final product.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: AI models can learn from past experiences and feedback. Thus, they continuously improve their performance and provide developers valuable insights to refine and enhance financial software.
- Adaptability to Market Dynamics: AI-powered analytics can monitor market trends and user behavior in real-time. It enables developers to adapt financial software to changing market conditions quickly and effectively, ensuring its relevance and competitiveness.
- Seamless Integration of Technologies: AI facilitates the seamless integration of various technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, into financial software development. It enables developers to create comprehensive and innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Real-world Examples of AI in Financial Software Development
Integrating AI in financial software development has led to innovative solutions and enhanced services across the finance industry. Here are some real-world examples demonstrating the impact of AI:
- J.P. Morgan’s COIN: J.P. Morgan Chase’s Contract Intelligence (COIN) platform uses machine learning to interpret commercial loan agreements. This AI system has reduced the manual work required, completing tasks in seconds that used to take hours, thereby saving hours of legal work annually.
- Zest AI: Zest AI applies machine learning to the underwriting process, helping lenders make faster and more accurate credit decisions. By analyzing thousands of data points, Zest AI can predict credit risk more effectively than traditional methods. Thus, it allows for broader access to credit and reduces bias in lending decisions.
- Kasisto’s KAI: KAI is an AI-powered conversational assistant used by financial institutions to enhance customer service. Capable of understanding and responding to a wide range of customer inquiries, KAI improves engagement and helps banks offer personalized financial advice, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Envestnet | Yodlee’s Data Aggregation: Envestnet | Yodlee uses AI to aggregate and analyze financial data from various sources. This enables financial service providers to offer personalized advice and insights, helping users manage their finances more effectively.
- Upstart: Upstart is a lending platform that uses AI to assess the risk of personal loans. By considering non-traditional factors such as education and employment, Upstart’s AI model approves more applicants than traditional credit-scoring systems and at lower interest rates.
Future Prospects of AI in Financial Software Development
The future prospects of AI in financial software development point towards a landscape where technology enhances financial services. Also, it creates new avenues for innovation and efficiency. Here’s what we can anticipate in the near future:
- Improvement of Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technologies are set to become more sophisticated, enabling AI systems to understand and process human language more accurately. This advancement will improve customer service bots, making them more intuitive and capable of handling complex customer inquiries and transactions seamlessly.
- Focus on Deep Learning: Deep learning will take center stage in AI development within FinTech, enabling more complex, data-driven decision-making processes. This focus will allow financial institutions to uncover insights from vast datasets at a new scale, leading to more personalized and efficient services.
- Further Automation of Financial Services: Automation in FinTech will extend beyond simple tasks to more complex financial operations, including personalized financial planning, robo-advisory services, and automated underwriting and claims processing. This shift will enhance operational efficiency and offer consumers more tailored and responsive financial products.
- More Accurate Predictive Analysis: With the advancement of AI algorithms, predictive analysis in financial software development will become more precise, enabling financial institutions to forecast market trends, credit risks, and consumer behavior with higher accuracy. This capability will improve risk management and offer a competitive edge in market analysis and investment strategies.
- Closer Cooperation with Blockchain Technology: The integration of AI with blockchain technology will deepen, leveraging blockchain’s capabilities for secure, transparent transactions and record-keeping with AI’s analytical power. Blockchain is revolutionizing banking and financial services by offering a fast and efficient framework for transactions. At the same time, AI enhances these processes with smart contract automation, fraud detection, and customer service improvements. Also, using blockchain in authentication and authorization processes will strengthen security measures, ensuring that financial transactions and access to sensitive information are secure and streamlined.
Read More: The Impact of AI on Industries: What You Need to Know
Final Thoughts
AI’s impact on financial software development is significant. It has transformed banking and investment methods by automating processes, enhancing security, and providing personalized experiences. This integration encourages innovation and accessibility in financial services.
AI’s impact on financial software development is significant. It has transformed banking and investment methods by automating processes, enhancing security, and providing personalized experiences. This integration encourages innovation and accessibility in financial services.