Seamless Cloud Migration: Tips, Tricks, and Best Practices
Table of Contents
Cloud migration helps businesses scale, cut costs, and improve security by moving data and applications from traditional servers to the cloud. It offers flexibility, better performance, and reduced IT expenses, making it a smart choice for growth.
However, migration comes with challenges like downtime, security risks, and integration issues. Without proper planning, businesses may face disruptions or unexpected costs.
This blog provides actionable tips, tricks, and best practices to help you migrate seamlessly. You’ll learn how to:
- Plan and execute a smooth migration
- Avoid common pitfalls and reduce downtime
- Secure and optimize your cloud setup
By the end, you’ll have the insights needed to transition to the cloud efficiently and future-proof your business.
What is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration is the process of moving your business’s data, applications, and workloads from on-premise servers (or even from one cloud provider to another) to a new cloud environment.
Instead of managing physical hardware, businesses store and access their data over the internet using cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Why Move to the Cloud?
- Cost Savings – No need to spend on expensive servers and IT maintenance.
- Flexibility & Scalability – Easily adjust resources based on business needs.
- Better Security – Cloud providers offer advanced security features.
- Remote Access – Employees can work from anywhere with secure cloud access.
Types of Cloud Migration
Not all businesses migrate to the cloud in the same way. There are different migration strategies, depending on how much you want to modify your current applications.
1. Rehosting (Lift and Shift)
- This is the simplest method of cloud migration.
- Applications and data are moved to the cloud without any modifications.
- Quick and cost-effective, but may not fully use cloud capabilities.
Example: Moving a company’s website from in-house servers to AWS without changing the code.
2. Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift)
- Applications are slightly modified to take advantage of some cloud benefits.
- Improves performance without a complete rebuild.
Example: Moving a database to a cloud-based version for better speed and efficiency.
3. Refactoring (Rearchitecting)
- Applications are completely redesigned to be cloud-native.
- Offers maximum flexibility, scalability, and performance.
Example: Rebuilding an old customer service app as a cloud-based AI chatbot.
4. Retiring and Retaining
- Retiring – Some outdated applications may no longer be useful and can be shut down.
- Retaining – Some apps may stay on-premise due to security or regulatory reasons.
Example: A legacy payroll system that doesn’t integrate well with cloud tools may be retained.
Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud: Which One is Right for You?
When moving to the cloud, businesses can choose from three main cloud models based on their needs:
1. Public Cloud
- Hosted by third-party providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Cost-effective and scalable.
- Suitable for startups and small businesses.
Example: A retail business storing customer orders on AWS.
2. Private Cloud
- Exclusive to one company, offering more security and control.
- Higher cost but better customization.
- Ideal for industries with strict regulations (finance, healthcare).
Example: A bank storing sensitive customer data in a private cloud.
3. Hybrid Cloud
- A mix of both public and private cloud.
- Balances flexibility, security, and cost.
- Best for businesses needing both on-premise and cloud storage.
Example: A company keeping customer-facing apps in the public cloud but storing sensitive financial data in a private cloud.
Key Steps to a Seamless Cloud Migration
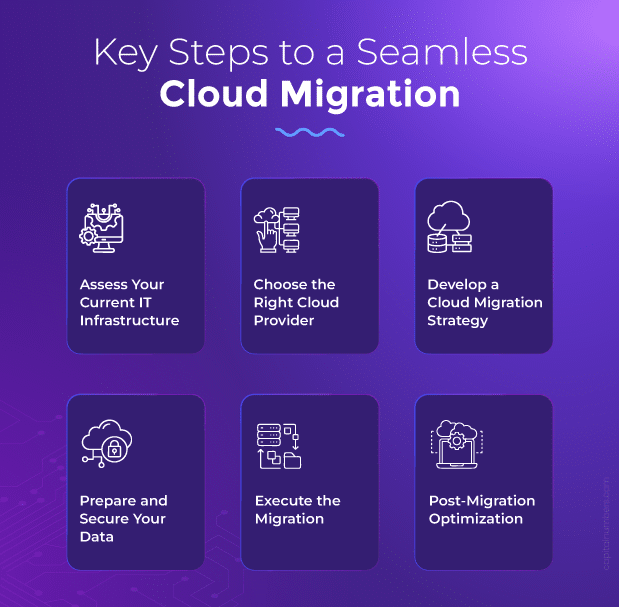
To ensure a smooth, secure, and efficient migration, follow these key steps.
Step 1: Assess Your Current IT Infrastructure
Before you move to the cloud, you need to understand what you currently have. This includes taking a detailed look at your existing IT systems, software, and business processes.
- Create an inventory – List all applications, databases, and workloads running on your current system.
- Identify dependencies – Some applications depend on others to work properly. Ensure they can move together.
- Check performance needs – Identify how much storage, processing power, and network capacity your business requires.
- Review compliance requirements – Ensure your business follows industry regulations (like GDPR for data privacy or HIPAA for healthcare).
Why this is important: Understanding your IT setup prevents surprises, helps reduce migration risks, and ensures a smooth transition to the cloud.
Step 2: Choose the Right Cloud Provider
Not all cloud providers offer the same features, pricing, or security levels. The right provider depends on your business needs, budget, and goals.
Popular Cloud Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Best for flexibility and large-scale businesses.
- Microsoft Azure – Ideal for businesses using Microsoft products.
- Google Cloud – Great for AI, analytics, and machine learning.
- Oracle Cloud – Strong choice for enterprise applications and databases.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Cost – Compare pricing models (pay-as-you-go, subscriptions, etc.).
- Security – Ensure strong encryption, identity management, and compliance features.
- Performance – Check speed, uptime, and service reliability.
- Scalability – Can the cloud grow with your business?
- Support & Compliance – Ensure the provider meets industry standards and offers customer support when needed.
Why this is important: The right cloud provider will save you money, improve efficiency, and provide better security for your business data.
Step 3: Develop a Cloud Migration Strategy
Once you choose a provider, the next step is to create a cloud migration plan to move your business smoothly without disruption.
Define Your Goals & Success Metrics:
- What do you want to achieve? (Lower costs, better performance, enhanced security?)
- How will you measure success? (Reduced downtime, improved system speed?)
Choose a Migration Approach:
Bang Migration – Move everything at once.
- Faster, but may cause temporary downtime.
- Best for smaller businesses with fewer systems.
Phased Migration – Move applications step by step.
- Reduces risk by testing each stage.
- Best for larger businesses with complex systems.
Why this is important: A clear migration plan minimizes risks, avoids downtime, and ensures a smooth transition without affecting business operations.
Step 4: Prepare and Secure Your Data
Data is one of the most valuable assets of your business, and ensuring it stays safe during migration is crucial.
Key Steps to Secure Data Before Migration:
- Back up everything – Create a copy of all business-critical data before migration.
- Ensure data accuracy – Fix duplicate or outdated data before moving to the cloud.
- Check security compliance – Make sure data storage follows legal regulations like GDPR (for customer data protection) and HIPAA (for healthcare information security).
- Encrypt data – Protect sensitive business data with strong encryption before and during migration.
Why this is important: Protecting data prevents loss, breaches, and compliance violations, ensuring a smooth and secure transition to the cloud.
Step 5: Execute the Migration
Now it’s time to move your applications and data to the cloud. However, this step requires careful monitoring to ensure everything works as expected.
Key Steps to Execute Migration Smoothly:
- Test the migration in a sandbox environment – Before moving real data, run tests in a simulated cloud environment.
- Implement security and access controls – Set permissions so only authorized employees can access sensitive data.
- Migrate in batches – If using a phased approach, move applications step by step, checking performance after each move.
- Monitor performance continuously – Track system performance, application response time, and potential errors during migration.
Why this is important: A well-executed migration reduces downtime, minimizes security risks, and ensures all systems work properly in the cloud.
Step 6: Post-Migration Optimization
Once everything is successfully migrated, the final step is to ensure your cloud system is running at its best.
Best Practices for Post-Migration Optimization:
- Test all applications – Ensure data and applications function correctly in the cloud.
- Optimize cloud resources – Adjust server sizes, storage, and computing power to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Monitor security – Keep an eye on potential threats and update security settings regularly.
- Train employees – Teach your team how to use cloud-based applications efficiently.
- Set up cloud governance – Establish policies for data access, backup, and future updates.
Why this is important: Regular monitoring and optimization ensure that your cloud setup is cost-effective, secure, and fully optimized for your business needs.
Common Cloud Migration Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Moving to the cloud can bring many benefits, but it also comes with challenges. If cloud migration is not planned properly, businesses can face downtime, security risks, unexpected costs, and technical difficulties. Below are the most common cloud migration challenges and how to tackle them effectively.
1. Downtime and Business Disruption
The Challenge:
One of the biggest concerns during cloud migration is downtime—when your business systems are temporarily unavailable. If your website, apps, or internal tools stop working during migration, it can lead to lost revenue, frustrated customers, and productivity issues for employees.
How to Overcome It:
- Plan a phased migration – Instead of moving everything at once, transfer systems step by step, starting with non-critical applications. This reduces risk and minimizes disruptions.
- Use a failover system – A failover system ensures that if something goes wrong, a backup system can take over without downtime.
- Schedule migration during off-peak hours – If your business has less activity during nights or weekends, move critical systems during these times to minimize the impact.
- Test before full migration – Use a sandbox environment to test the migration before moving everything live. This helps catch potential issues early.
Why this is important: Careful planning prevents system failures, ensures business continuity, and keeps customers happy.
2. Security and Compliance Risks
The Challenge:
Migrating sensitive business data to the cloud raises concerns about data security and regulatory compliance. If security is not properly handled, businesses may be exposed to cyber threats, data breaches, and non-compliance fines.
How to Overcome It:
- Use strong encryption – Encrypt data before, during, and after migration to prevent unauthorized access.
- Set up access controls – Ensure only authorized employees can access sensitive business data by implementing role-based access permissions.
- Follow a compliance checklist – Depending on your industry, ensure that your cloud provider follows regulations like:
- GDPR (for customer data protection in Europe)
- HIPAA (for healthcare data security)
- ISO 27001 (for information security management)
- Choose a secure cloud provider – Select a provider with built-in security features, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), firewalls, and automatic backups.
Why this is important: A secure migration protects sensitive business data, ensures legal compliance, and builds customer trust.
You May Also Read: 12 Best Practices to Secure Your API in the AWS Cloud
3. Cost Overruns and Budget Management
The Challenge:
Cloud migration can become more expensive than expected if businesses don’t track spending properly. Many companies make the mistake of over-provisioning resources (buying more computing power and storage than needed), leading to wasted money.
How to Overcome It:
- Optimize resource allocation – Right-size your cloud resources by analyzing actual usage and avoiding unnecessary storage or computing power.
- Use cost-saving features – Most cloud providers offer ways to reduce costs:
- Reserved instances – Pre-pay for cloud resources at a discount instead of paying for them on demand.
- Auto-scaling – Automatically increases or decreases cloud resources based on real-time demand.
- Set up budget alerts – Use cloud provider tools to track spending and get alerts before exceeding your budget.
- Compare pricing models – Choose between pay-as-you-go, subscription, or hybrid pricing models based on your business needs.
Why this is important: Cloud cost optimization helps businesses stay within budget, reduce unnecessary expenses, and maximize cloud investment returns.
4. Integration Issues with Legacy Systems
The Challenge:
Many businesses use older software and systems (legacy systems) that may not be fully compatible with cloud platforms. Migrating these systems without proper planning can cause technical issues, performance problems, or even system failures.
How to Overcome It:
- Assess compatibility – Identify which legacy applications can move to the cloud easily and which require modifications.
- Use APIs and middleware – APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and middleware help connect old systems with new cloud-based applications, ensuring smooth communication between different platforms.
- Adopt a hybrid cloud approach – If some systems can’t move to the cloud immediately, use a hybrid cloud model (mixing on-premise and cloud services) to transition gradually.
- Upgrade outdated software – If a system is too old to integrate with the cloud, consider updating or replacing it with a cloud-friendly alternative.
Why this is important: Proper integration ensures seamless operations, prevents compatibility issues, and maximizes the benefits of cloud migration.
You May Also Read: Legacy App Modernization: How Could It Benefit Your Business?
5. Skill Gaps and Training Requirements
The Challenge:
Cloud technology is different from traditional IT systems, and many businesses lack skilled employees who understand cloud infrastructure, security, and optimization. Without proper training, employees may struggle to use cloud-based tools effectively.
How to Overcome It:
- Invest in cloud training – Provide training programs for IT teams and employees to help them understand cloud-based workflows and security best practices.
- Use managed cloud services – If your team lacks cloud expertise, work with managed service providers who handle security, monitoring, and optimization for you.
- Hire cloud migration experts – If needed, bring in cloud consultants or engineers to ensure a smooth and professional migration.
- Encourage continuous learning – Cloud technology evolves quickly, so encourage employees to stay updated with certifications and online courses (AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Google Cloud Certification, etc.).
Why this is important: A well-trained team reduces operational mistakes, improves security, and ensures your business maximizes cloud benefits.
Migrating to the cloud is not just about transferring data—it’s about building a future-ready digital infrastructure that is secure, scalable, and cost-efficient. However, without the right expertise, cloud migration can be complex and challenging. This is where cloud engineering services play a crucial role. From selecting the best cloud provider to optimizing post-migration performance, expert cloud engineers ensure a seamless transition with minimal risk.
Cloud Migration Best Practices for a Smooth Transition
Migrating to the cloud can bring cost savings, flexibility, and improved efficiency to your business, but only if done correctly. To ensure a smooth and successful transition, follow these best practices.
1. Start Small, Scale Gradually
Instead of moving all your business systems to the cloud at once, start with a small portion and test how it works. This is called a pilot migration—it allows you to identify issues before rolling out the full migration.
- Run a test migration with one application or department before migrating everything.
- Analyze performance to see how cloud systems handle your business workload.
- Fix any issues in the pilot stage before scaling to the rest of your business.
2. Use Automation to Simplify Migration
Manually migrating large amounts of data and applications can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automation tools help speed up the migration process, reduce manual work, and minimize mistakes.
Best Cloud Migration Automation Tools:
- AWS Migration Hub – Tracks and manages your migration to Amazon Web Services.
- Azure Migrate – Helps businesses assess, migrate, and optimize workloads in Microsoft Azure.
- Google Cloud Migrate – Automates the transfer of workloads to Google Cloud.
3. Ensure Strong Security Measures
When moving to the cloud, security should be a top priority to prevent cyber threats and data breaches.
- Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM) – This ensures that only authorized employees can access sensitive business data.
- Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest – Encryption ensures that data is secure while being transferred and stored in the cloud.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding an extra layer of security prevents unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits – Check your cloud security settings frequently to spot vulnerabilities.
4. Monitor and Optimize Performance Post-Migration
Once your business has successfully moved to the cloud, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure everything is running smoothly.
Best Cloud Monitoring Tools:
- AWS CloudWatch – Monitors performance and security for applications in AWS.
- Azure Monitor – Tracks cloud performance and helps optimize costs.
- Google Cloud Operations Suite – Provides real-time system monitoring.
Key Steps for Optimization:
- Track system performance – Identify any slowdowns or failures.
- Optimize cloud resources – Adjust cloud services to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Conduct regular audits – Review system logs and performance reports to detect issues early.
5. Have a Disaster Recovery and Backup Plan
No system is 100% failure-proof. Having a backup and recovery strategy ensures that your business can quickly recover in case of system failures, cyberattacks, or accidental data loss.
- Multi-Region Backup Strategy – Store backups in different locations to protect against regional outages.
- Automated Failover Mechanisms – Set up automatic switchovers to backup systems in case of failures.
- Regular Data Backups – Schedule daily, weekly, or monthly backups depending on your business needs.
- Test Disaster Recovery Plans – Run periodic disaster recovery drills to ensure your team knows how to restore lost data quickly.
You May Also Read: Cloud Computing in 2025: What’s Next for the Industry?
Conclusion: A Successful Cloud Migration Starts with a Smart Plan
Migrating to the cloud can help businesses reduce costs, improve security, and boost performance—but only with proper planning. To ensure success:
- Assess your IT setup before migration.
- Choose the right cloud provider based on your needs.
- Use automation tools to simplify the process.
- Prioritize security and compliance.
- Monitor and optimize performance after migration.
Moving to the cloud can be complex, but you don’t have to do it alone. Our cloud experts are here to help you make the transition smooth, secure, and cost-effective. Contact us today and let’s make your migration a success!